What Is Staking in Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency staking has emerged as one of the most accessible and effective ways to earn passive income in the world of blockchain technology. By staking your crypto assets, you can participate in the operation of a blockchain network while earning rewards, often in the form of additional cryptocurrency. But what exactly is staking, and how does it work?
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about staking cryptocurrency—from the basics to the best practices—to help you start earning passive income today.
Understanding the Basics of Staking
What Is Staking?
Staking is the process of locking up your cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. Unlike Bitcoin, which relies on a proof-of-work (PoW) system that requires significant energy and computational resources, staking is tied to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
In PoS, validators are chosen to verify transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. This mechanism is more energy-efficient and rewards participants (stakers) with additional coins for helping to secure the network.
For a detailed explanation of how PoS works, you can visit Binance Academy’s guide.
How Staking Differs from Mining
Mining involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions, which requires expensive hardware and consumes a significant amount of electricity. Staking, on the other hand, is simpler: you lock up your coins in a wallet, and the network uses them to validate transactions. No special hardware is needed, making staking an attractive option for beginners.
Benefits of Staking
- Earn Passive Income: By staking your crypto, you earn rewards in the form of additional tokens.
- Support the Network: Staking helps maintain the security and efficiency of the blockchain.
- Eco-Friendly: Unlike mining, staking consumes significantly less energy.
- Low Entry Barrier: Many platforms allow you to stake directly from your wallet or through exchanges.
How Does Staking Work?
When you stake your cryptocurrency, you essentially “lock” it in a wallet or on an exchange to participate in the network’s consensus process. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Choose a Blockchain Network: Only PoS or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) networks support staking. Examples include Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), and Solana (SOL).
- Lock Your Assets: Stake your coins through a compatible wallet or exchange.
- Validate Transactions: The network selects validators based on their staked amount. These validators verify transactions and add them to the blockchain.
- Earn Rewards: In return for staking, you earn a share of the transaction fees or newly minted coins.

Popular Cryptocurrencies for Staking
If you’re ready to start staking, here are some of the most popular cryptocurrencies that support staking:
- Ethereum (ETH): With Ethereum 2.0, Ethereum has transitioned to a proof-of-stake mechanism. Validators are required to stake a minimum of 32 ETH to participate directly, but smaller holders can stake through staking pools. Learn more about Ethereum staking at Ethereum.org.
- Cardano (ADA): Cardano offers a straightforward staking system with no minimum staking requirement. ADA holders can delegate their stake to pools.
- Solana (SOL): Solana boasts high throughput and scalability. You can stake SOL through wallets like Phantom or Solflare.
- Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot features a robust staking mechanism, allowing participants to nominate validators.
- Tezos (XTZ): Tezos is known for its low staking requirements and liquid staking options.
Ways to Stake Cryptocurrency
1. Staking on Exchanges
Staking via cryptocurrency exchanges is one of the easiest ways to get started. Major exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken offer staking services that are user-friendly and require minimal technical expertise.
- Pros:
- No need to set up a wallet or node.
- Low entry barriers and accessible interfaces.
- Rewards are often automatically distributed.
- Cons:
- You don’t fully control your private keys.
- Exchange outages or hacks could pose a risk.
2. Staking Through Wallets
Wallets like Trust Wallet, Ledger, and MetaMask allow you to stake directly while retaining control of your private keys. Wallet staking provides more security and autonomy than exchanges.
- Pros:
- You maintain full control over your funds.
- Often higher rewards compared to exchanges.
- Cons:
- Requires more setup effort.
- May involve additional fees.
3. Joining Staking Pools
If you don’t have enough cryptocurrency to meet the minimum staking requirement of certain blockchains, staking pools are a great option. Pools combine resources from multiple participants, increasing the likelihood of being chosen as a validator.
- Example Pool Providers:
- Pros:
- Lower entry requirements.
- Earn rewards without running your own node.
- Cons:
- A portion of your rewards goes to the pool operator.
4. Running a Validator Node
For more experienced users, running your own validator node offers the highest rewards but also comes with greater complexity and responsibility.
- Requirements:
- High staking minimums (e.g., 32 ETH for Ethereum).
- Reliable hardware and internet connection.
- Pros:
- Maximum rewards for direct participation.
- Cons:
- Requires technical expertise.
- Financial penalties (slashing) for validator misbehavior.
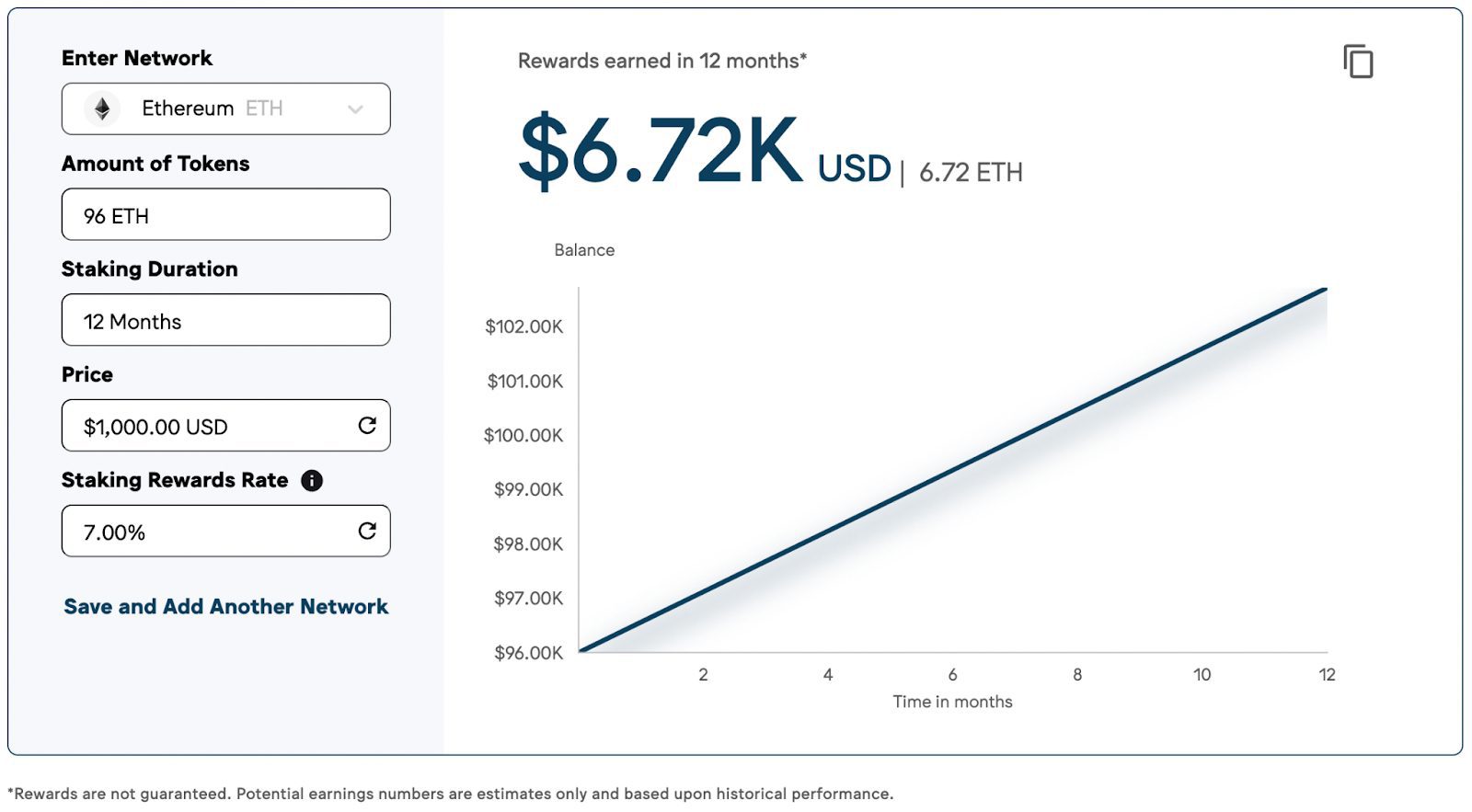
How Much Can You Earn from Staking?
Staking rewards vary depending on the cryptocurrency and platform you choose. On average:
- Ethereum (ETH): 4–6% annually.
- Cardano (ADA): 4–5% annually.
- Polkadot (DOT): 10–14% annually.
- Solana (SOL): 6–8% annually.
Some platforms and staking pools may offer bonus rewards during promotional periods, so it’s worth checking for opportunities.
To calculate potential earnings, use a staking rewards calculator like Staking Rewards.
Risks of Staking Cryptocurrency
While staking offers great benefits, it’s important to be aware of the associated risks:
- Price Volatility: Crypto prices are highly volatile. If the value of your staked asset drops, your rewards may not offset the loss.
- Lock-Up Periods: Some blockchains require you to lock your funds for a fixed period, during which they cannot be withdrawn.
- Slashing: Validators who act maliciously or fail to meet network requirements may face penalties, reducing staked funds.
- Platform Security: Staking on exchanges or third-party platforms introduces custodial risks. Choose reputable providers with strong security measures.
Best Practices for Safe Staking
- Research Before You Stake: Always research the blockchain network and staking platform to understand the risks and rewards.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Avoid staking all your assets in one network to minimize risk.
- Use Hardware Wallets: For maximum security, use a hardware wallet to stake directly.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly check your staking rewards and ensure the validator or pool is performing well.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with network updates and staking requirements. Some blockchains may introduce changes that affect rewards or security.
Tax Implications of Staking
Staking rewards are often considered taxable income in many jurisdictions. The IRS in the United States, for example, treats staking rewards as income at the time they are received. Make sure to:
- Keep detailed records of your staking rewards.
- Use crypto tax software like CoinTracker or CryptoTrader.Tax for accurate reporting.
Start Earning Passive Income Through Staking
Cryptocurrency staking is a fantastic way to earn passive income while contributing to the security of blockchain networks. Whether you choose to stake through exchanges, wallets, or staking pools, the key is to start small, research thoroughly, and stay informed. With popular coins like Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana offering attractive rewards, staking has become a powerful tool for both beginners and experienced investors to grow their crypto holdings.
Ready to begin? Explore staking opportunities on trusted platforms like Binance or Kraken today.



